Empowering Breakthroughs
Featured Articles
CADworks3D takes immense pride in earning the trust of global partners and the opportunity to collaborate with reputable companies and accomplished researchers. Our commitment to excellence is reflected in the remarkable success achieved by our esteemed collaborators, and we are honored to be a part of their journey.

2023
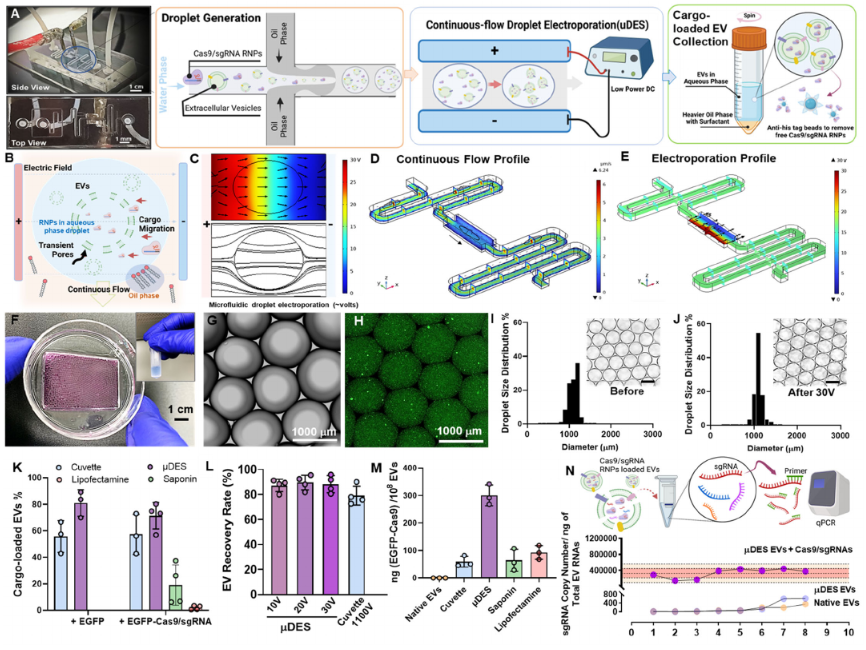
Room temperature roll-to-roll additive manufacturing of polydimethylsiloxane-based centrifugal microfluidic device for on-site isolation of ribonucleic acid from whole blood

2023
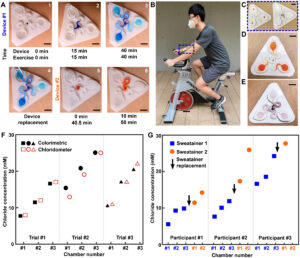
Skin-interfaced microfluidic systems with spatially engineered 3D fluidics for sweat capture and analysis

2022
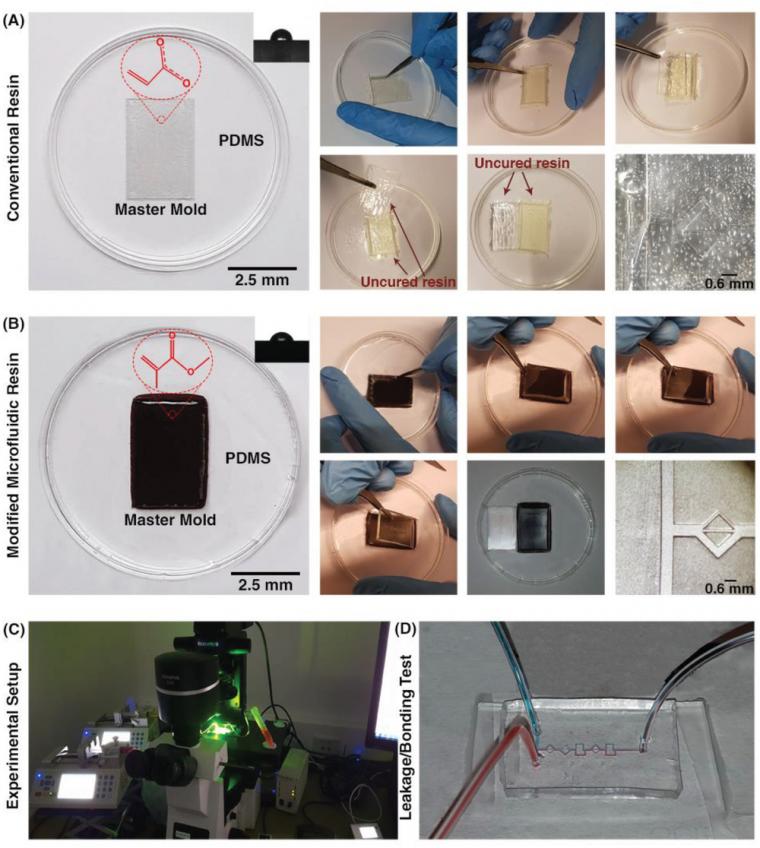
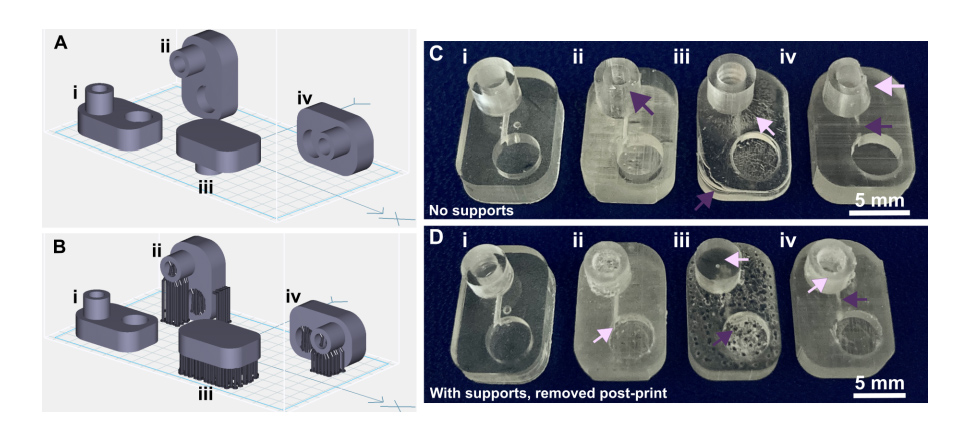
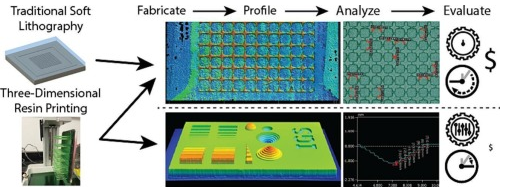
Applied tutorial for the design and fabrication of biomicrofluidic devices by resin 3D printing
2024

2024
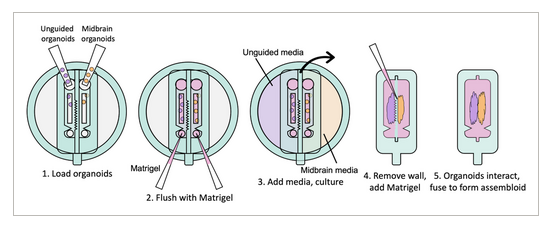
Microfabricated dynamic brain organoid cocultures to assess the effects of surface geometry on assembloid formation

2024
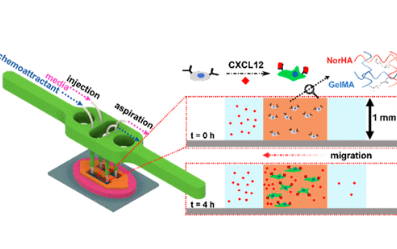
Open-Top Patterned Hydrogel-Laden 3D Glioma Cell Cultures for Creation of Dynamic Chemotactic Gradients to Direct Cell Migration

2024
Evaluation of industrial and consumer 3-D resin printer fabrication of microdevices for quality management of genetic resources in aquatic species

2024
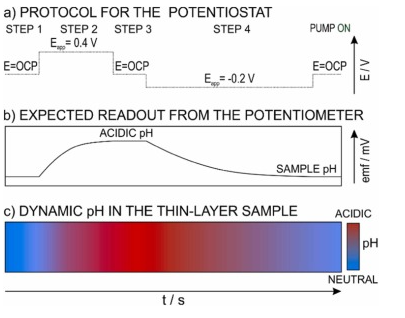
Reversible electrochemical pH modulation in thin-layer compartments using poly(aniline-co-o-aminophenol)

2024
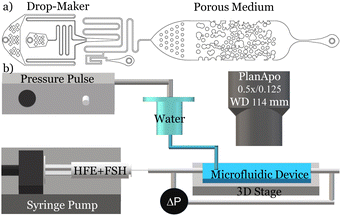
Emergence of preferential flow paths and intermittent dynamics in emulsion transport in porous media
2023

2023
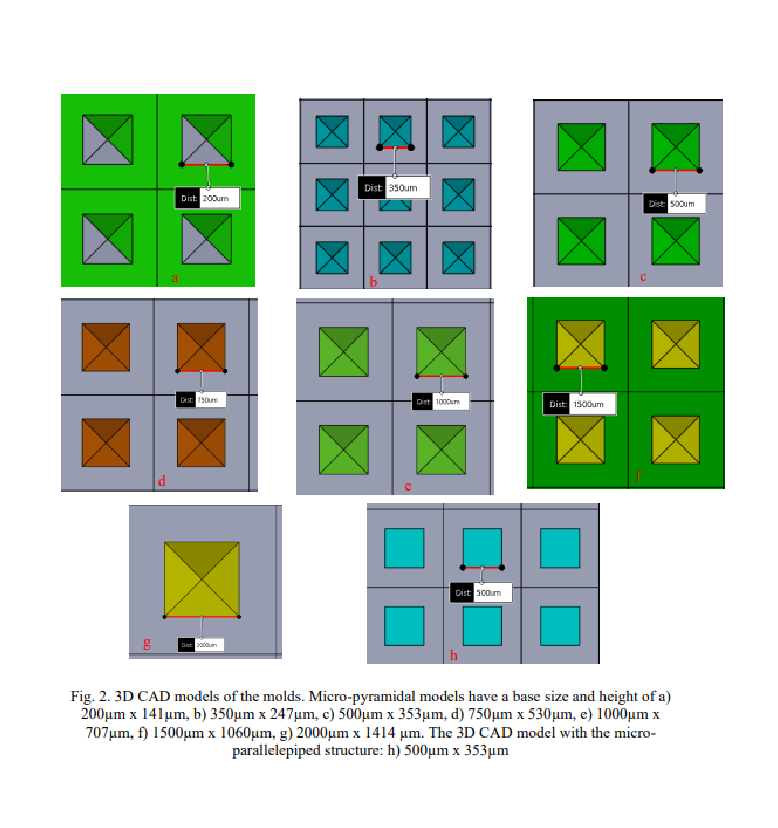
Rapid manufacturing of flexible microstructured pdms substrates, using 3d DLP printing technique, for flexible pressure sensors
2023
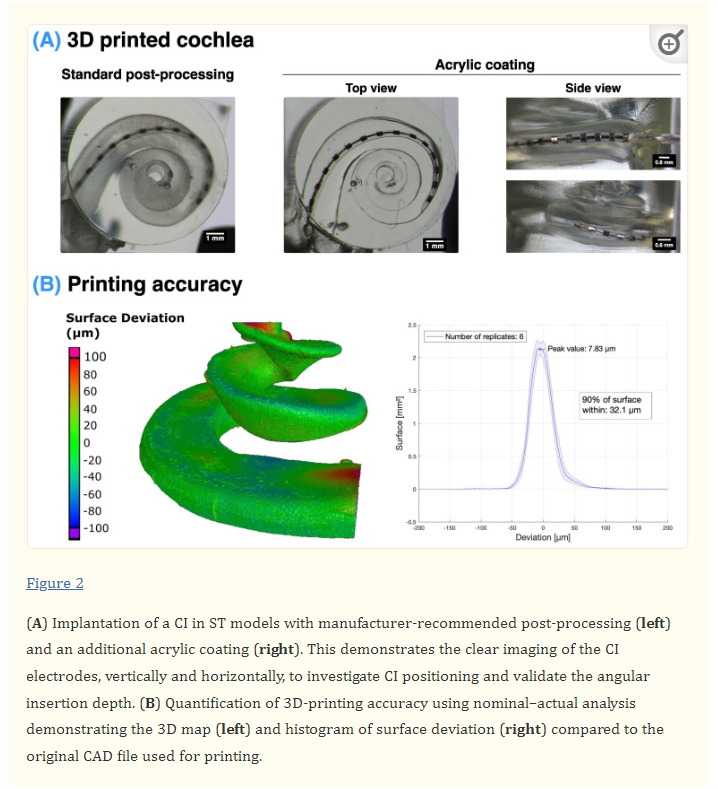
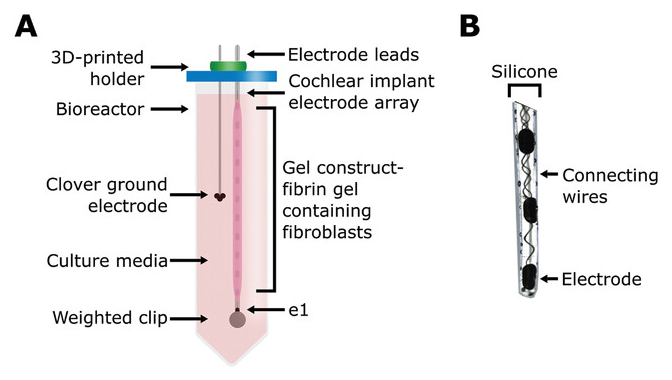
Tissue-Engineered Cochlear Fibrosis Model Links Complex Impedance to Fibrosis Formation for Cochlear Implant Patients

2023
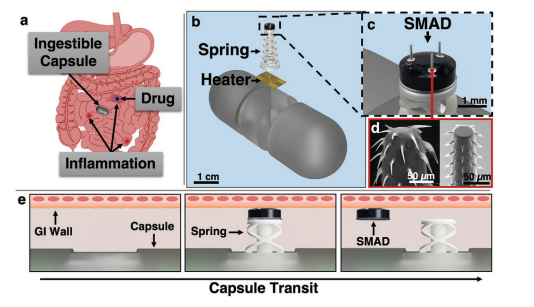
Thermomechanical Soft Actuator for Targeted Delivery of Anchoring Drug Deposits to the GI Tract


2023
Applied tutorial for the design and fabrication of biomicrofluidic devices by resin 3D printing

2023
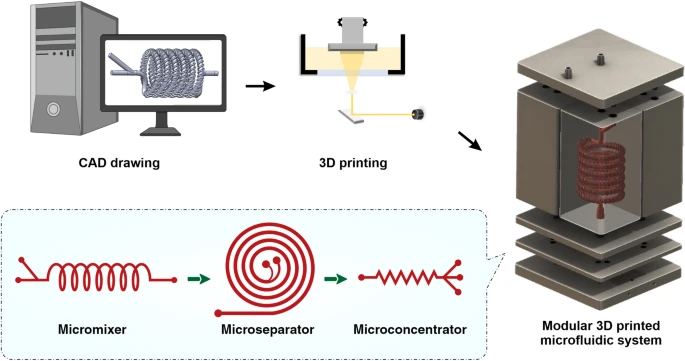
A modular 3D printed microfluidic system a potential solution for continuous cell harvesting in large-scale bioprocessing

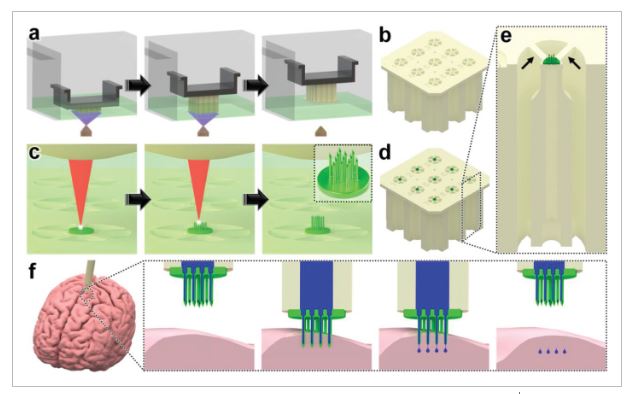
2023
3d printed microinjection needle arrays via a hybrid dlp direct laser writing strategy case study
2022

2022
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI): 3D Printing-Enabled Uniform Temperature Distributions in Microfluidic Devices

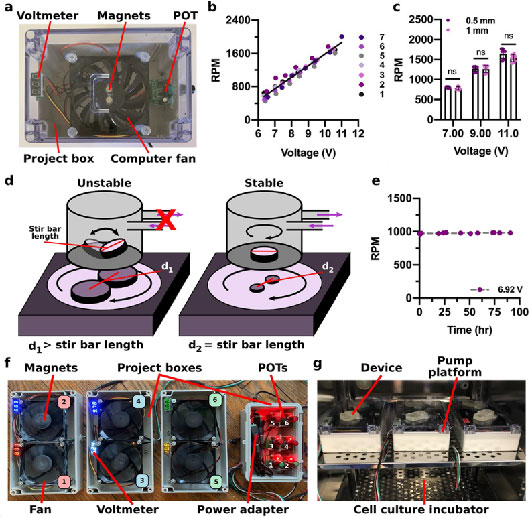
2022
Microscale impeller pump for recirculating flow in organs-on-chip and microreactors

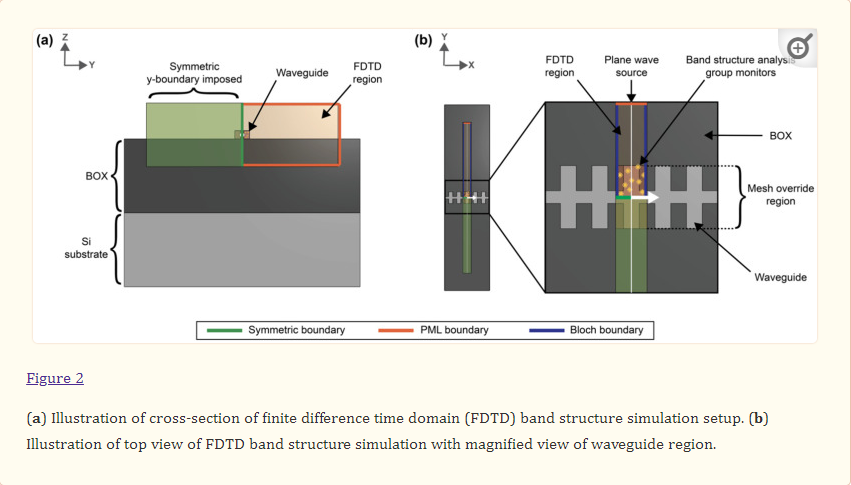
2022
An Optimization Framework for Silicon Photonic Evanescent-Field Biosensors Using Sub-Wavelength Gratings

2022
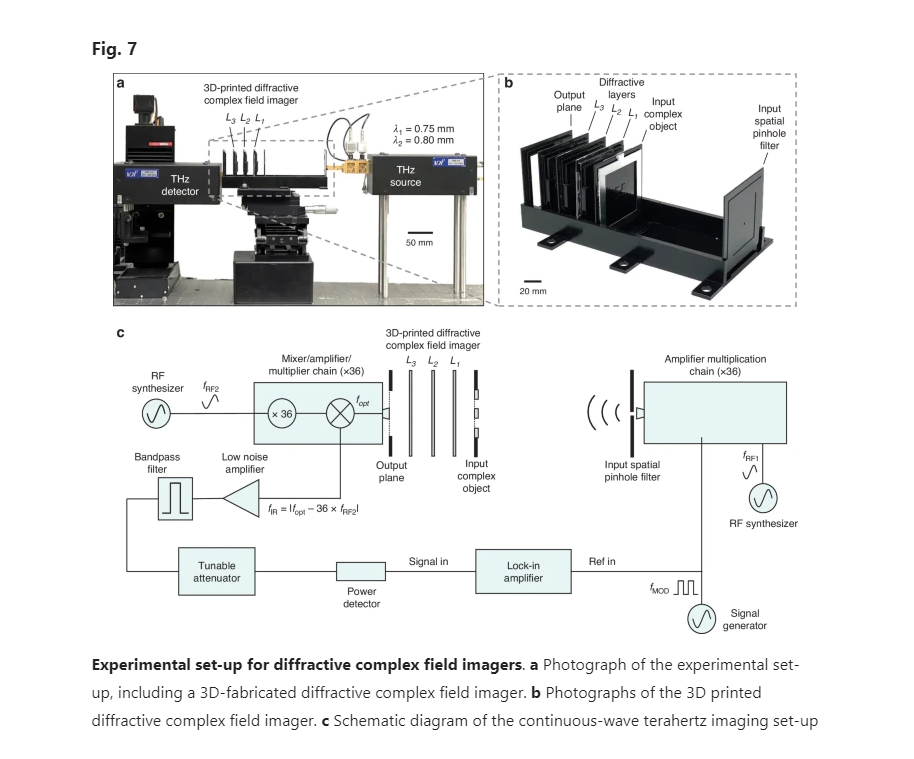
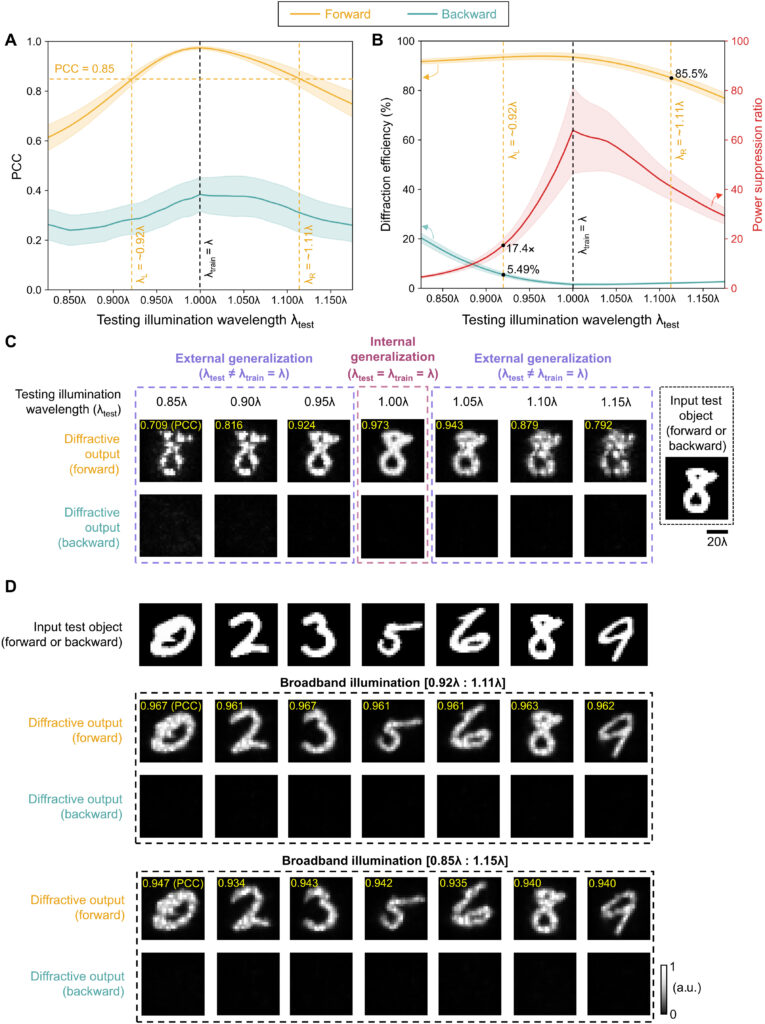
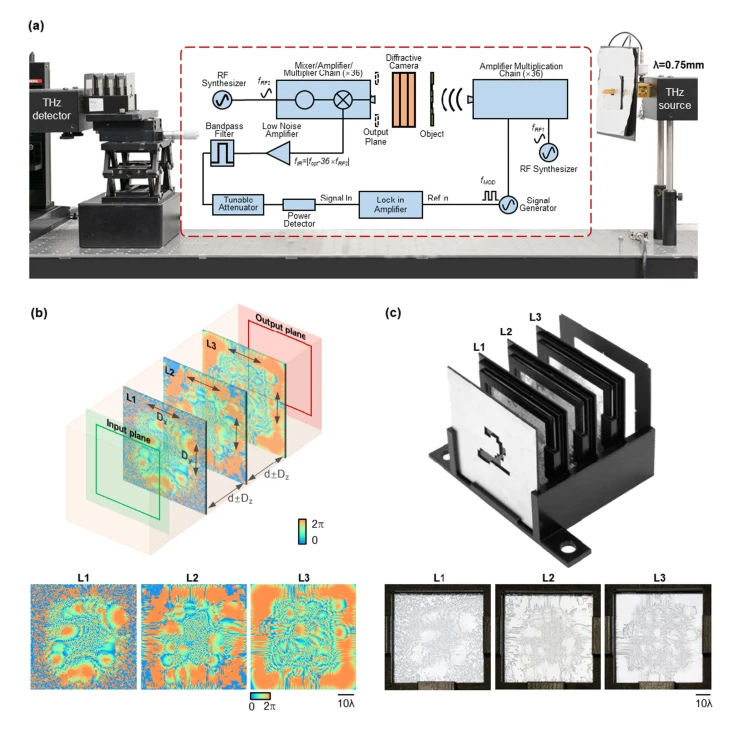
To image, or not to image: class-specific diffractive cameras with all-optical erasure of undesired objects

2022
PDMS Organ-On-Chip Design and Fabrication: Strategies for Improving Fluidic Integration and Chip Robustness of Rapidly Prototyped Microfluidic In Vitro Models

2022
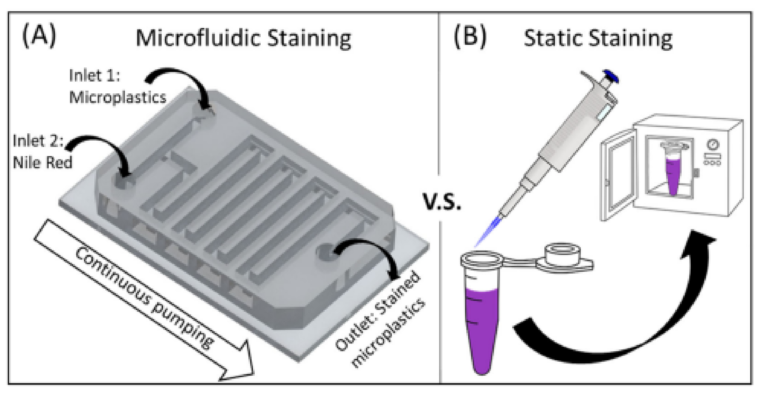
A Low-Cost Microfluidic Method for Microplastics Identification: Towards Continuous Recognition
2021

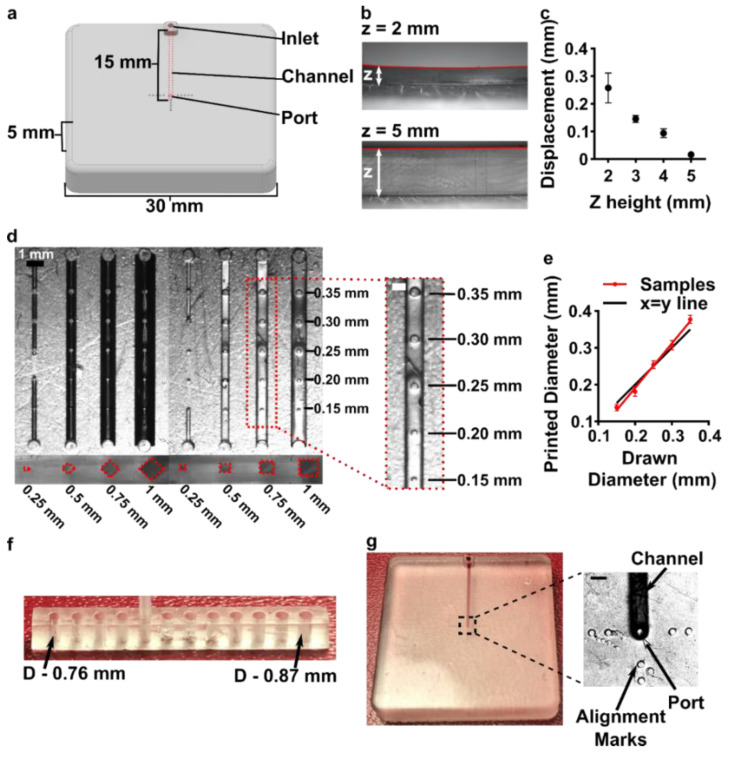
2021
Rapid Fabrication by Digital Light Processing 3D Printing of a SlipChip with Movable Ports for Local Delivery to Ex Vivo Organ Cultures

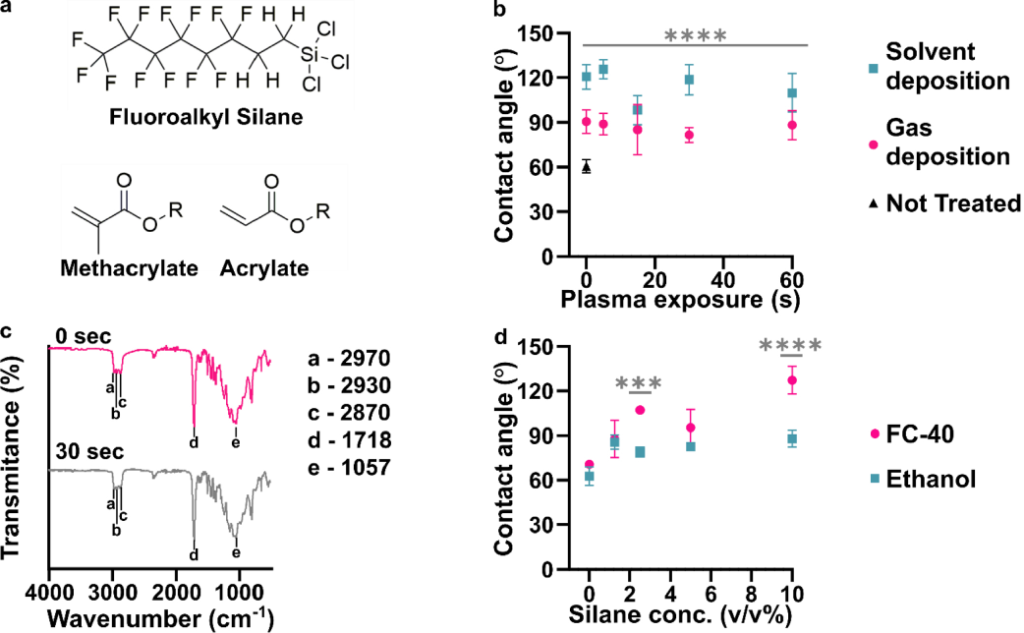
2021
Selective Fluorination of the Surface of Polymeric Materials after Stereolithography 3D Printing
2020

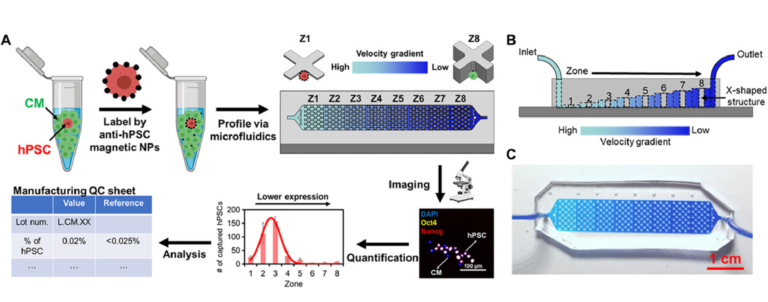
2020
Ultrasensitive and rapid quantification of rare tumorigenic stem cells in hPSC-delivered cardiomyocyte populations
2019

2019
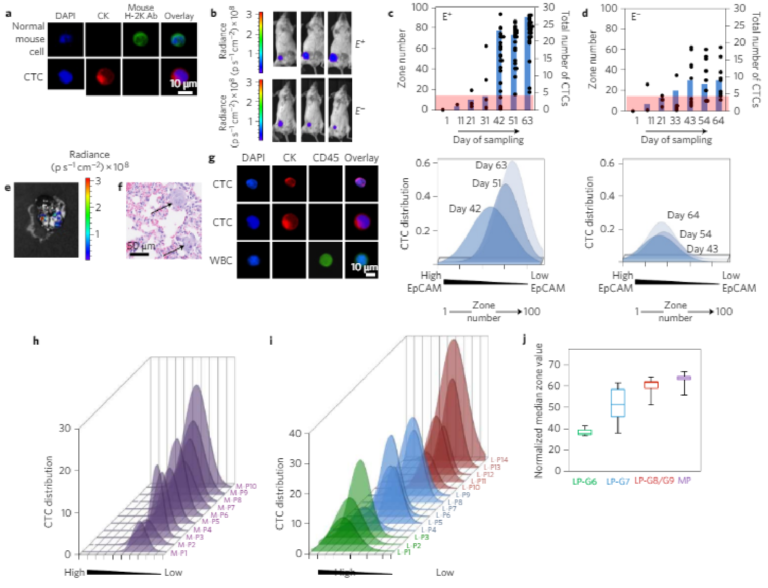
Quantifying EpCAM heterogeneity of circulation-tumor-cells (CTCs) from small cell lung cancer (SCLC) patients.
2018

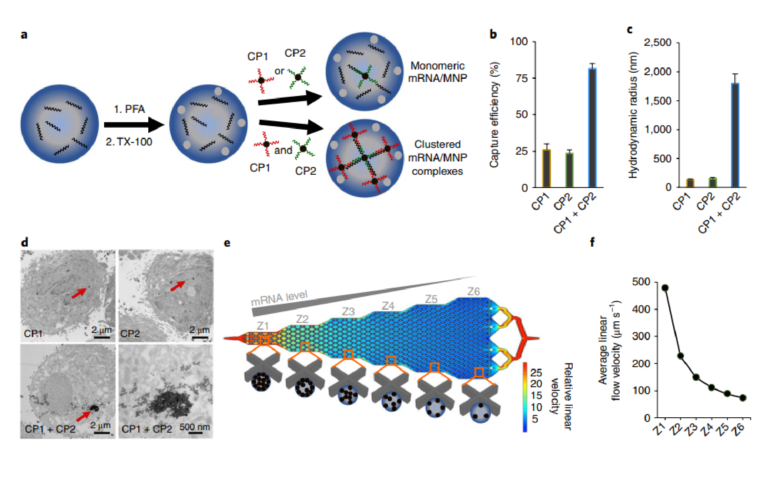
2018
Single-cell mRNA cytometry via sequence-specific nanoparticle clustering and trapping
2016

2016
Inkjet printing of UC-curable adhesive and dielectric inks form microfluidics devices