Microfluidics Made Easy
Microfluidics Made Easy
“3D printing can seem complex, but we’re here to make it simple and accessible.”
As the use of 3D printing in research continues to grow rapidly, our complete 3D printing system is helping researchers around the world achieve outstanding results. With our advanced 3D printers and specialized 3D materials, innovation has never been more within reach.
Step 01 | CAD Your Design
Use your preferred CAD software to design a device that meets your needs. Then, import the file into slicing software to prepare it for 3D printing.
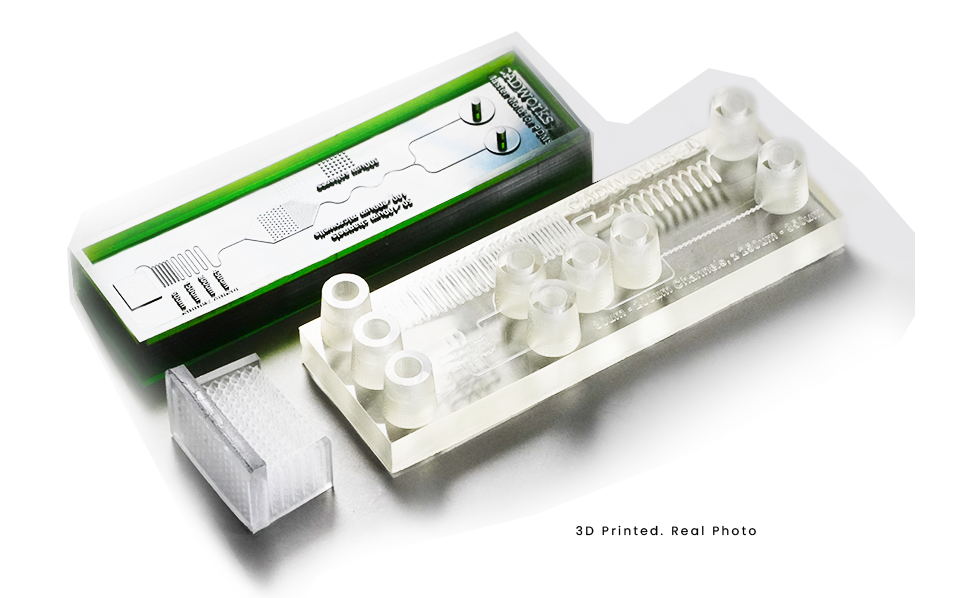
Step 02 | 3D Print Your Devices
Start 3D printing your device at your benchside using our specialized 3D printer and materials designed for microfluidics. Simply upload your file, click “start,” and let the printer handle the rest.
Step 03 | Cleaning and Curing Your Devices
Remove the device from the buildplate, flush the channels with IPA, and cure it following the specific guidelines for each device.
Step 04 | Ready To Use
Start your research and enjoy the convenience of quickly creating another device if you need to adjust the design to meet your requirements.

Your Research, at Benchside
3D PRINTING MICROFLUIDIC DEVICES IN 1 DAY
Our specialists will answer all your questions.
In research, time and accuracy are everything. Traditional fabrication methods can be slow, costly, and limiting, especially when working with complex microfluidic designs. If these challenges sound familiar, 3D printing could be the missing piece in your research.
” Just 3 Steps: Pour, Print, Clean. The devices are Ready for your research.”
With our 3D Printers and specialized 3D Materials for microfluidics, researchers can create custom devices in hours, not weeks. Unlike CNC machining, which is slow and often requires outsourcing, 3D printing lets you design, print, and test right at your bench. No cleanroom, no long wait times—just fast, precise, and repeatable results.
Whether researchers are developing new applications or improving existing designs, 3D printing gives them full control to speed up their research and innovation
“We can do a lot of continuous measurements and repeated measurements with these interconnectors using 3D printing.”
PhD Candidate, Surath Gomis, at the Kelley Lab in University Of Toronto
“I can 3D print a chip in only 20 minutes.”
PhD Candidate, David Philpott, at the Kelley Laboratory in University of Toronto
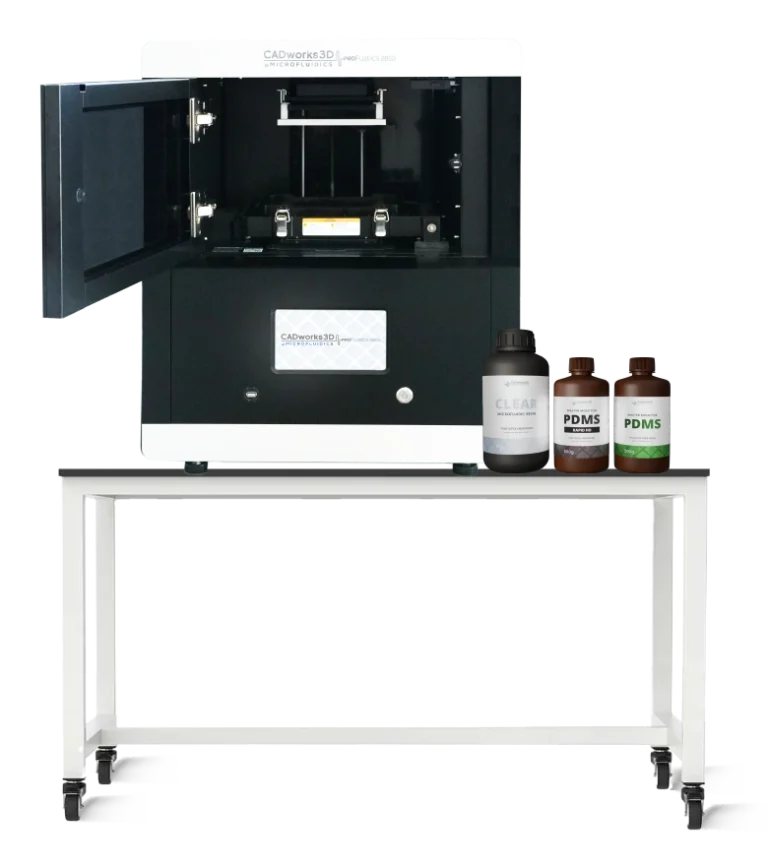
3D PRINTERS
3D MATERIALS






